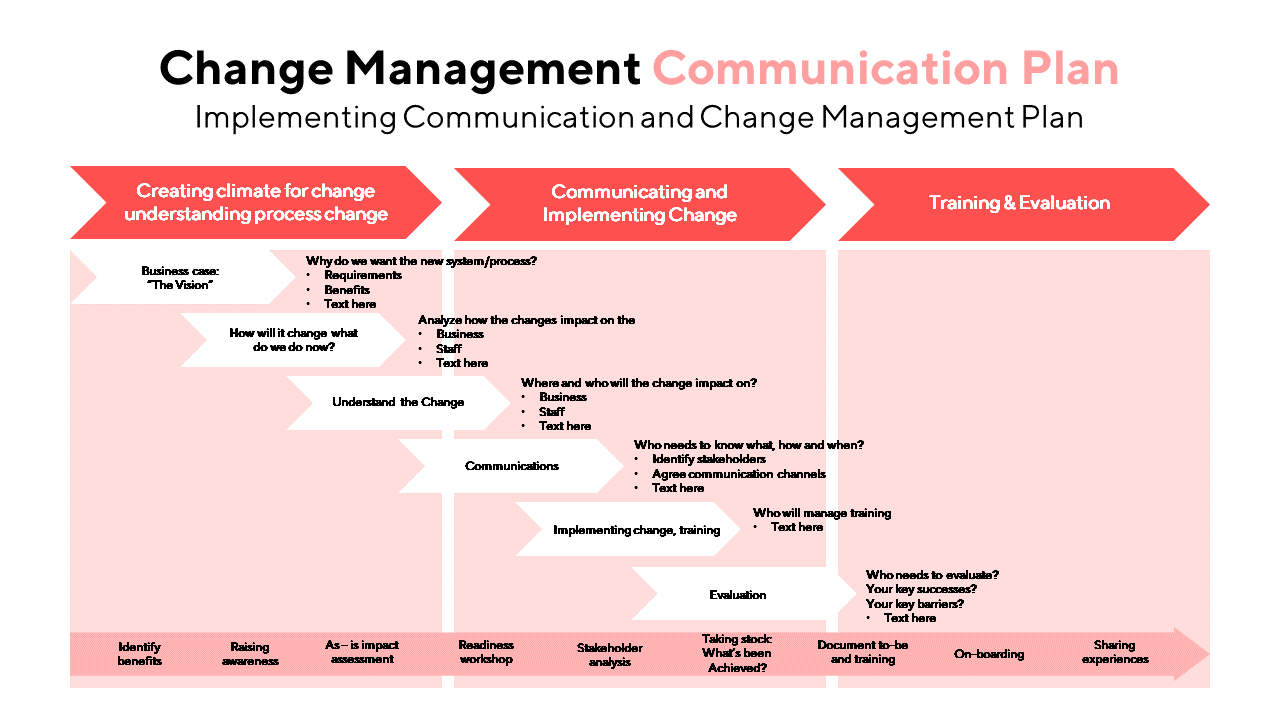
Change is an inevitable part of any organization’s journey. Whether it’s a shift in strategy, a technological upgrade, or a structural reorganization, change is constant. However, the success of these changes often hinges on how effectively they are communicated and managed. This is where a well-crafted change management communication plan comes into play.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of building an effective change management communication plan. We’ll explore the seven key components that can transform a potentially turbulent transition into a smooth, well-understood, and accepted process. So, let’s embark on this transformative journey together.
Understanding the Essence of Change Management Communication
Before diving into the components of a change management communication plan, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental concepts of change management and its connection to effective communication. Change management is the structured approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations from their current state to a desired future state. Effective communication is the lifeblood of this transition.
When people understand the ‘why,’ ‘what,’ and ‘how’ of change, they are more likely to embrace it. A change management communication plan serves as the roadmap for disseminating information, building support, and minimizing resistance during periods of change.
Now, let’s explore the seven key components that make up a robust change management communication plan:
1. Stakeholder Analysis and Segmentation
Change doesn’t affect everyone in an organization equally. Some individuals or groups will be more impacted than others. Therefore, the first step in creating a change management communication plan is to conduct a thorough stakeholder analysis.
Stakeholder analysis involves identifying all individuals or groups who will be affected by the change. These stakeholders can be categorized based on their level of influence, support, or resistance to the change. Typical stakeholder groups might include employees, managers, executives, customers, suppliers, and shareholders.
Once stakeholders are identified, segmentation helps tailor communication strategies to address their unique needs and concerns. Effective segmentation allows for personalized messaging, which can greatly enhance buy-in and support.
2. Clear and Compelling Vision Statement
The foundation of any change management communication plan is a clear and compelling vision statement. This statement articulates the reasons behind the change, the intended outcomes, and the benefits for both the organization and its stakeholders.
A well-crafted vision statement should be:
- Clear: Easily understandable by everyone in the organization.
- Compelling: Inspires and motivates individuals to align with the change.
- Realistic: Attainable within the given context and resources.
The vision statement serves as a beacon, guiding all communication efforts throughout the change process.
3. Change Messaging and Storytelling
Effective communication is not just about relaying information; it’s about telling a compelling story. Change messaging should go beyond the mere transmission of facts and figures. It should engage the emotions and imagination of the audience.
Crafting a change story involves:
- Understanding the audience: Tailoring messages to resonate with different stakeholder groups.
- Highlighting benefits: Emphasizing how the change will improve individual and organizational outcomes.
- Addressing concerns: Acknowledging potential challenges and providing solutions.
- Consistency: Ensuring that messages align with the overall vision and are delivered consistently across all communication channels.
Storytelling can breathe life into your change initiative, making it relatable and memorable.
4. Communication Channels and Timing
Selecting the right communication channels is crucial to ensure that messages reach the intended recipients effectively. Different stakeholders may prefer various channels, such as email, in-person meetings, intranet, social media, or video conferencing. The choice of channels should align with stakeholder preferences and the nature of the message.
Timing is equally critical. Messages should be timed strategically to coincide with key milestones in the change process. Early communication should focus on creating awareness, while later stages should provide more detailed information and support.
5. Two-Way Communication and Feedback Mechanisms
Effective change management communication is not a one-way street. It’s essential to create opportunities for two-way communication. This means listening to the concerns, questions, and feedback of stakeholders.
Establishing feedback mechanisms, such as surveys, suggestion boxes, or regular Q&A sessions, encourages open dialogue. Actively responding to feedback demonstrates that the organization values the input of its employees and stakeholders, fostering a sense of involvement and ownership in the change process.
6. Training and Development
Change often requires individuals to acquire new skills, behaviors, or knowledge. A well-rounded change management communication plan should incorporate a robust training and development component.
Training programs should be designed to equip employees with the necessary tools to succeed in the new environment. Communication should not only inform employees about the change but also prepare them to embrace it. Providing opportunities for skill development and learning reinforces the organization’s commitment to supporting its workforce through the transition.
7. Metrics and Evaluation
To ensure the effectiveness of your change management communication plan, you need to establish clear metrics and evaluation criteria. Metrics help in quantifying the impact of the plan and identifying areas that may require adjustment.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) could include:
- Employee engagement: Measuring the level of enthusiasm and commitment towards the change.
- Knowledge transfer: Assessing the extent to which employees have grasped the new information or skills.
- Resistance levels: Monitoring any signs of resistance or pushback.
- Communication effectiveness: Evaluating the reach and impact of your messages through surveys and feedback.
Regularly analyzing these metrics allows you to fine-tune your communication strategy and adapt to changing circumstances.
Change Management Communication Plan
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the seven key components of a change management communication plan. Remember that effective change management is not about imposing change on individuals; it’s about guiding them through a transformational journey.
By conducting stakeholder analysis, crafting a compelling vision, embracing storytelling, selecting the right communication channels, promoting two-way communication, investing in training and development, and continuously evaluating your efforts, you can create a change management communication plan that paves the way for successful change initiatives.
Change is constant, but with the right communication strategy in place, you can navigate it with confidence and lead your organization towards a brighter future.
Now, it’s time for you to put these principles into action and embark on your own change management journey.