Innovation is the lifeblood of modern business, driving growth, and competitive advantage. However, it can be challenging to navigate the ever-changing landscape of emerging technologies, especially when hype and buzz can distort the reality of what is possible. That’s where the Gartner Hype Cycle comes in – a powerful tool that can help businesses manage their expectations and accelerate innovation by providing a realistic view of the maturity and potential of emerging technologies. In this chapter, we’ll explore the history, methodology, and applications of the Gartner Hype Cycle, as well as practical tips for how to leverage it effectively.
What do we mean by hype?
In the context of the Gartner Hype Cycle, “hype” refers to the excessive attention and expectations that can surround new and emerging technologies or innovations. This hype can be driven by a variety of factors, including media coverage, investor interest, and enthusiastic marketing efforts by technology vendors and startups.
Hype can create unrealistic expectations about the potential of a new technology or innovation, leading to a rush to invest and adopt before the technology has been fully tested or matured. This can result in projects that fail to meet expectations or do not deliver the promised benefits, causing disillusionment and a decline in interest.
It’s important to note that hype is not necessarily a negative thing. It can help to raise awareness and generate excitement about new technologies, driving innovation and investment. However, it’s important to manage expectations and approach new technologies with a critical eye, evaluating their potential benefits and risks and developing realistic plans for adoption and implementation.
The Gartner Hype Cycle provides a framework for understanding the typical trajectory of new technologies, including the hype phase, and can help businesses manage their expectations and make informed decisions about when and how to adopt new technologies.
History and Methodology of the Gartner Hype Cycle:
The Gartner Hype Cycle was first introduced in 1995 by the research firm Gartner, Inc. as a way to track the adoption and maturity of emerging technologies. The methodology is based on the premise that new technologies go through a predictable pattern of hype, disillusionment, and eventual adoption, known as the “hype cycle.” This cycle is driven by a combination of factors, including media attention, investor interest, and real-world feedback from early adopters.
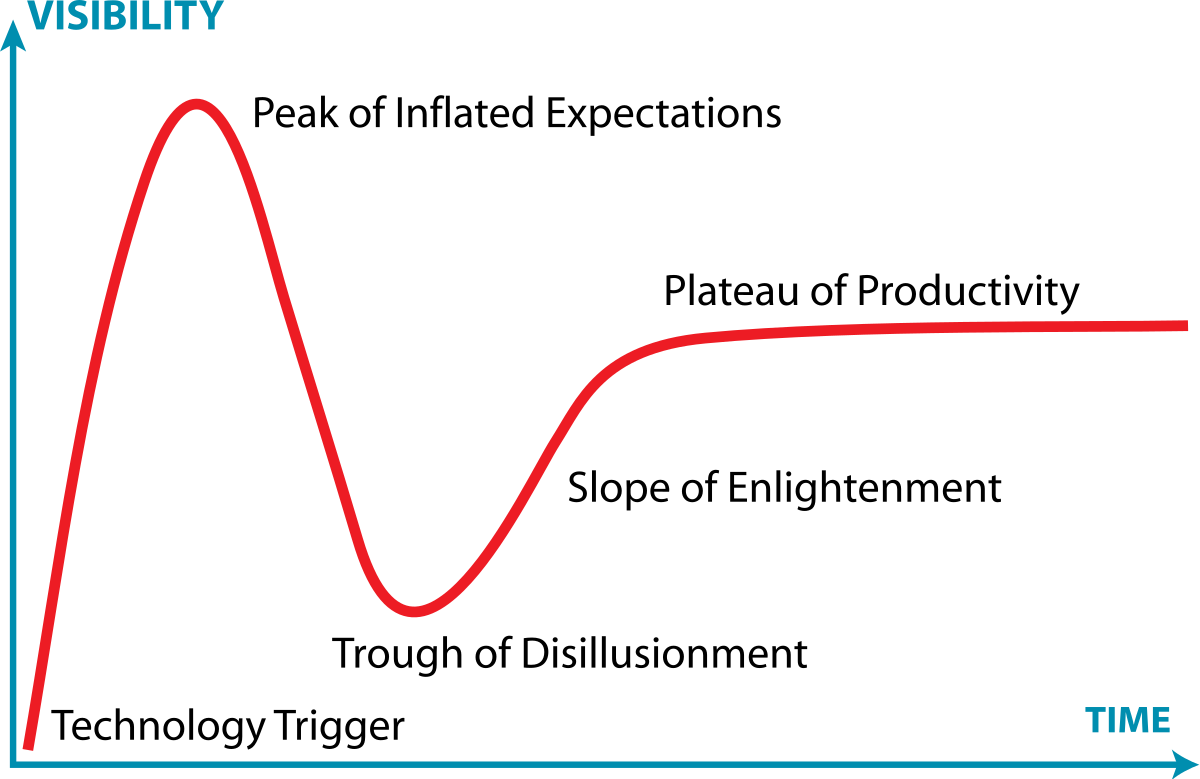
The Gartner Hype Cycle is represented as a graph, with the x-axis representing time and the y-axis representing expectations. The graph is divided into five distinct phases: the “Innovation Trigger,” the “Peak of Inflated Expectations,” the “Trough of Disillusionment,” the “Slope of Enlightenment,” and the “Plateau of Productivity.”
The first phase, the Innovation Trigger, represents the initial buzz and excitement around a new technology. This is followed by the Peak of Inflated Expectations, where hype and unrealistic expectations lead to a rapid increase in attention and investment. However, as the limitations and challenges of the technology become apparent, it enters the Trough of Disillusionment, where interest wanes, and many projects fail. Eventually, as the technology matures and its potential becomes clearer, it enters the Slope of Enlightenment, where more realistic expectations and successful implementations drive renewed interest. Finally, the technology reaches the Plateau of Productivity, where it becomes a widely adopted and integral part of the business landscape.
Applications of the Gartner Hype Cycle:
The Gartner Hype Cycle has become an essential tool for businesses, investors, and analysts looking to understand the potential of emerging technologies. By providing a realistic view of the maturity and potential of new technologies, the Hype Cycle can help companies manage their expectations, make informed investment decisions, and accelerate innovation.
For example, businesses can use the Hype Cycle to identify technologies that are likely to have a significant impact on their industry in the coming years, and start planning for their adoption. By understanding the potential risks and challenges of new technologies, they can develop realistic timelines and budgets, and avoid investing in solutions that may not deliver the expected results.
Investors can also use the Hype Cycle to identify promising startups and emerging technologies, and make informed investment decisions based on their potential for growth and maturity. By understanding the typical trajectory of new technologies, they can avoid investing in companies that are still in the early stages of development and focus on those that are likely to reach the Plateau of Productivity.
Practical Tips for Leveraging the Gartner Hype Cycle:
To leverage the full potential of the Gartner Hype Cycle, businesses and investors need to understand its limitations and apply it in a thoughtful and nuanced way. Here are some practical tips for how to do that:
- Understand the context: The Hype Cycle is not a one-size-fits-all solution and should be used in the context of your specific industry and business goals. Consider factors such as your organization’s maturity level, market trends, and competitive landscape when interpreting the Hype Cycle.
- Don’t chase the hype: Avoid getting caught up in the initial hype around new technologies and instead focus on understanding their long-term potential and practical applications. While it can be tempting to invest in the latest and greatest technology, it’s essential to ensure that it aligns with your business strategy and can deliver tangible value.
- Stay informed: The Hype Cycle is not a static model, and new technologies are constantly emerging and evolving. Stay up-to-date with the latest developments in your industry and regularly revisit your Hype Cycle analysis to ensure that you’re adapting to new trends and opportunities.
- Collaborate with experts: Don’t rely solely on the Hype Cycle to make critical business decisions. Engage with industry experts, analysts, and other stakeholders to gain a broader perspective and validate your assumptions.
The Gartner Hype Cycle is a powerful tool that can help businesses manage their expectations and accelerate innovation by providing a realistic view of the maturity and potential of emerging technologies. By understanding the typical trajectory of new technologies, organizations can make informed investment decisions, develop realistic timelines and budgets, and avoid investing in solutions that may not deliver the expected results. However, it’s essential to apply the Hype Cycle in a thoughtful and nuanced way, taking into account the context of your specific industry and business goals. By following these practical tips, businesses can leverage the full potential of the Hype Cycle and power their innovation with realistic expectations.
The 5 phases and their implications for businesses
The Gartner Hype Cycle is divided into five distinct phases: the “Innovation Trigger,” the “Peak of Inflated Expectations,” the “Trough of Disillusionment,” the “Slope of Enlightenment,” and the “Plateau of Productivity.” Each of these phases has unique implications for businesses that are adopting new technologies.
- Innovation Trigger:
The Innovation Trigger marks the beginning of the Hype Cycle, where a new technology or concept is first introduced. This phase is characterized by a high level of excitement and anticipation, as people start to envision the potential benefits and applications of the technology.
Implications for businesses: In this phase, businesses need to keep a close eye on emerging technologies and assess their potential impact on their industry. Early adopters can gain a competitive advantage by being the first to explore and experiment with new technologies. However, it’s essential to approach new technologies with a critical eye and evaluate their feasibility and practicality before investing resources.
- Peak of Inflated Expectations:
The Peak of Inflated Expectations is the phase where hype and buzz around the technology reach their peak. Everyone wants to be part of the “next big thing,” and investors pour money into companies that promise to revolutionize the industry. However, the reality of the technology’s limitations and challenges soon becomes apparent.
Implications for businesses: In this phase, businesses need to avoid getting caught up in the hype and carefully evaluate the potential risks and challenges of adopting new technologies. It’s essential to establish realistic expectations and avoid investing too heavily in unproven technologies. Instead, businesses should focus on building a solid foundation for innovation, including developing the necessary infrastructure and capabilities to support the adoption of new technologies.
- Trough of Disillusionment:
The Trough of Disillusionment is the phase where the technology falls out of favor, and many projects fail. The initial hype has worn off, and people are starting to realize that the technology may not be the silver bullet they thought it would be. However, this phase is also an opportunity for companies to refine and improve the technology.
Implications for businesses: In this phase, businesses need to stay committed to innovation and avoid abandoning new technologies just because they’re experiencing challenges. Instead, they should focus on identifying and addressing the key obstacles to adoption and refine their strategies for using the technology. This is also a time to learn from the mistakes of early adopters and avoid repeating their missteps.
- Slope of Enlightenment:
The Slope of Enlightenment is the phase where the technology starts to mature, and its true potential becomes clearer. Successful implementations and case studies demonstrate the value of the technology, and more realistic expectations drive renewed interest.
Implications for businesses: In this phase, businesses need to start developing concrete plans for adopting and integrating the technology into their operations. It’s essential to identify the key use cases and applications of the technology and develop a roadmap for implementation. Collaboration with technology vendors and other stakeholders can help to ensure that businesses are making informed decisions and leveraging the technology to its full potential.
- Plateau of Productivity:
The Plateau of Productivity is the final phase of the Hype Cycle, where the technology has become widely adopted and an integral part of the business landscape. Best practices and standards have emerged, and the technology has proven its value and reliability.
Implications for businesses: In this phase, businesses can reap the benefits of their investment in new technologies. However, it’s essential to continue to monitor and evaluate the technology’s performance and make adjustments as necessary. Innovation is a continuous process, and businesses need to stay ahead of emerging trends and technologies to maintain their The Gartner Hype Cycle provides a valuable framework for businesses to manage their expectations and accelerate innovation. By understanding the typical trajectory of new technologies, businesses can make informed decisions about when and how to adopt new technologies, and avoid falling victim to hype and unrealistic expectations. However, it’s important to approach the Hype Cycle with a critical eye and take into account the specific context of the business and industry. By leveraging the Hype Cycle effectively and following best practices for innovation, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and drive growth and competitive advantage.
How can you identify where you are?
To identify where you are on the Gartner Hype Cycle, you need to evaluate the current state of a particular technology or innovation and compare it to the typical trajectory of the Hype Cycle. Here are some steps to help you determine where you are:
- Research the technology: Gather as much information as possible about the technology or innovation you are interested in. Understand its history, current state, and potential applications.
- Look for indicators of hype: Assess the level of media attention and buzz surrounding the technology. Are there many articles and news stories about it? Are there numerous companies and startups working on it? Is there a lot of investment and funding going into it?
- Evaluate real-world implementations: Look for examples of the technology being used in real-world applications. Are there successful case studies and use cases? Are there any challenges or limitations that have been identified?
- Compare to the Hype Cycle: Use the Gartner Hype Cycle as a reference point and compare the current state of the technology to the typical trajectory of the Hype Cycle. Where does it fit on the curve? Is it in the Innovation Trigger phase, the Peak of Inflated Expectations, the Trough of Disillusionment, the Slope of Enlightenment, or the Plateau of Productivity?
- Consider the specific context: Remember that the Hype Cycle is not a one-size-fits-all model and needs to be applied in the context of your specific industry and business goals. Consider factors such as your organization’s maturity level, market trends, and competitive landscape when interpreting the Hype Cycle.
By following these steps, you can gain a better understanding of where you are on the Hype Cycle and make more informed decisions about how to approach the technology or innovation in question.